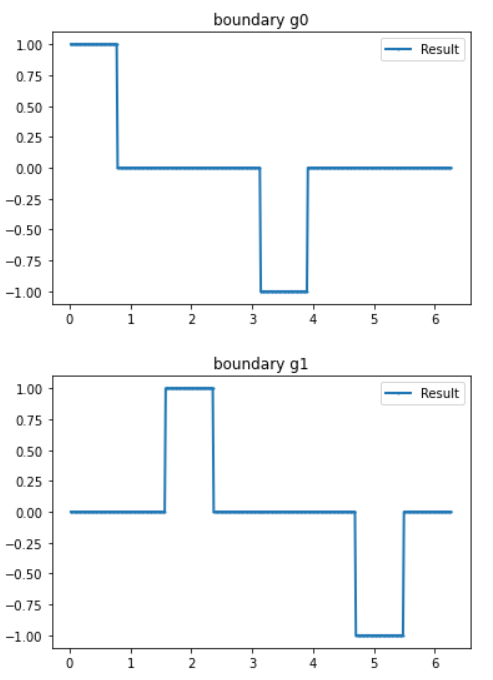
Module 2 - Forward
- module2_forward_cont.current_method(n_g, value=1, method=1)
This function an expression that represent the current in the vertex.
- Parameters:
n_g (int) – Measurements number.
value (float) – value in the vertex.
method (int) – Current pattern.
- Returns:
Expression – Return list of expressions.
- Method Values:
1 and -1 in opposite direction, where 50% of the boundary is always 0.
- module2_forward_cont.fn_addnoise(data, level, noise_type='uniform', seed=42)
Function receives a vector which represents the data in the electrodes and returns a noised vector with the chosen noise level and the type of noise. We use it in
ForwardProblem.add_noise().- Parameters:
data (array) – Vector with potencial in electrodes or any other vector.
level (float) – Noise level (%), expect values between 0 and 1.
noise_type – Noise type, uniform or cauchy.
seed (int.) – Seed for random function.
- Returns:
Array – Return noised vector.
- Example:
>>> print(np.ones(8)) >>> print(fn_addnoise(data=np.ones(8), level=0.01, noise_type='cauchy', seed=32)) [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] array([0.99905327, 1.02206251, 1.00356633, 1.00236212, 1.00101231, 0.99904405, 1.0105611 , 0.98656216])
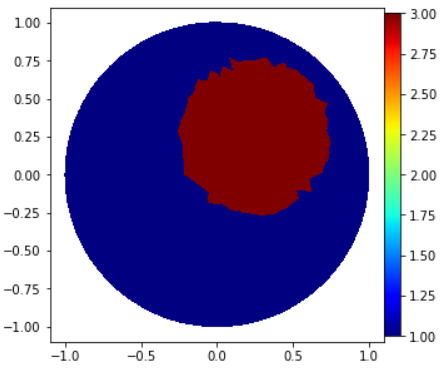
- module2_forward_cont.GammaCircle(mesh, in_v, out_v, radius, centerx, centery)
Function to create a circle in the mesh with some proprieties
- Parameters:
mesh (
dolfin.cpp.mesh.Mesh) – Mesh.in_v (float) – Value inside circle
out_v (float) – Value outside circle
radius (float) – Circle radius
centerx (float) – Circle center position x
centery (float) – Circle center position y
- Returns:
Array – Return a vector where each position correspond de value of the function in that element.
- Example:
>>> ValuesCells0=GammaCircle(mesh=mesh_direct, in_v=3.0, out_v=1.0, radius=0.50, centerx=0.25, centery=0.25) >>> print(ValuesCells0) [1. 1. 1. ... 1. 1. 1.]
>>> "Plot" >>> gamma0=CellFunction(mesh_direct, values=ValuesCells0); >>> V_DG=FiniteElement('DG',mesh_direct.ufl_cell(),0) >>> plot_figure(mesh_direct, V_DG, gamma0, name="Resposta gamma");
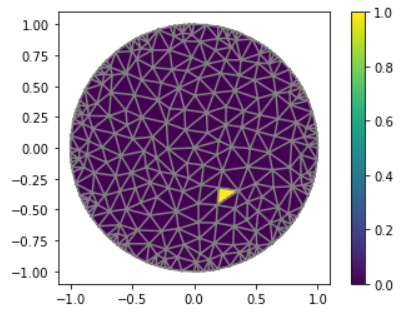
- class module2_forward_cont.CellFunction(mesh, values, **kwargs)
Auxiliar function to transform an array to a Function We use it with
GammaCircle()- Parameters:
mesh (
dolfin.cpp.mesh.Mesh) – Mesh.values (array) – Array with values of the function in the cell.
- Example:
>>> ValuesCells0=np.zeros(mesh_inverse.num_cells()) #Define a vector of zeros >>> ValuesCells0[5]=1 #Cell 5 has value 1 >>> gamma0=CellFunction(mesh_inverse, values=ValuesCells0);#Get vector and transform in a function cell
If you want plot the function:
>>> V_DG=FiniteElement('DG',mesh_inverse.ufl_cell(),0) #Space of Finite Elemente descontinuous garlekin degree 0 >>> Q=FunctionSpace(mesh_inverse,V_DG) #Functionspace to interpolate gamma >>> gamma0=interpolate(gamma0, Q) #Interpolation gamma to generate a function >>> p=plot(gamma0) #plot gamma0 >>> plot(mesh_inverse) #plot mesh >>> plt.colorbar(p) #set colorbar.
- class module2_forward_cont.ForwardProblem(mesh)
Object Forward Problem EIT 2D Continous Model.
- Parameters:
mesh (
dolfin.cpp.mesh.Mesh) – Mesh. We recommend fromMyMesh()- Example:
"Basic Definitions" VD=FiniteElement('CG',mesh_direct.ufl_cell(),1) F_Problem=ForwardProblem(mesh_direct) "Solver" list_u0=F_Problem.solve_forward(VD, gamma0, I_all) u0_boundary=F_Problem.boundary_array(mesh_inverse)
If you need it, see
GammaCircle()andCellFunction().- solve_forward(V, gamma, I_all)
Solver Forward Problem EIT 2D
- Parameters:
V (FiniteElement) – FiniteElement Fenics object
gamma (
CellFunction()) – Finite Element FunctionI_all (
current_method()or list of arrays) – Current density in each electrode for each measurement
- Returns:
(Array) – Return function that is solution from variational problem.
- Example:
>>> F_Problem=ForwardProblem(mesh_direct) >>> list_u0=F_Problem.solve_forward(VD, gamma0, list_gs)
- boundary_array(mesh_inverse=None, concatenate=True)
Get’s the boundary values of function solution and returns array. If you set a coarse mesh you will get the values in the vertices that are commum. If you set conccatenate=False, will receive a array with separeted results, is usefull if you used more than one current.
- Parameters:
mesh (
dolfin.cpp.mesh.Mesh) – Corse Mesh. We recommend fromMyMesh()concatenate (bool) – Default True
- Returns:
(Array) – Vertex values of the function.
- Example:
>>> u0_boundary=F_Problem.boundary_array(mesh_inverse)
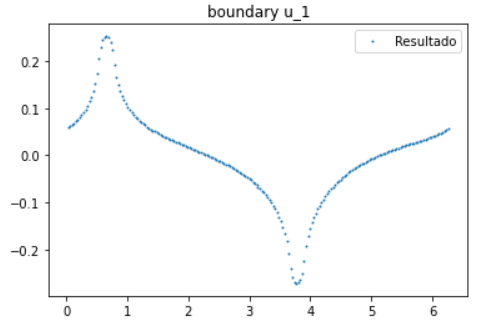
- plot_boundary(mesh_inverse=None, index=0)
Get’s the boundary values of function solution and returns a graph. If you set a coarse mesh you will get the values in the vertices that are commum and plot it.
- Parameters:
mesh (
dolfin.cpp.mesh.Mesh) – Corse Mesh. We recommend fromMyMesh()index (int) – Index of solution, if you need it.
- Example:
>>> data_u0=F_Problem.plot_boundary(mesh_inverse, index=1)
- add_noise(noise_level=0, noise_type='uniform', seed=42, mesh=None)
Function that add noise in the potential values.
- Parameters:
data (array) – Vector with potencial in electrodes or any other vector.
level (float) – Noise level (%), expect values between 0 and 1.
noise_type (str.) – Noise type, uniform or cauchy.
mesh (
dolfin.cpp.mesh.Mesh) – Corse Mesh. We recommend fromMyMesh()
- Returns:
Array – Return a vector with potentials values concatenated.
- Example:
"Noise Parameters" noise_level=0.01 noise_type='uniform' seed=1 u0_boundary=F_Problem.add_noise(noise_level noise_type, seed, mesh_inverse)